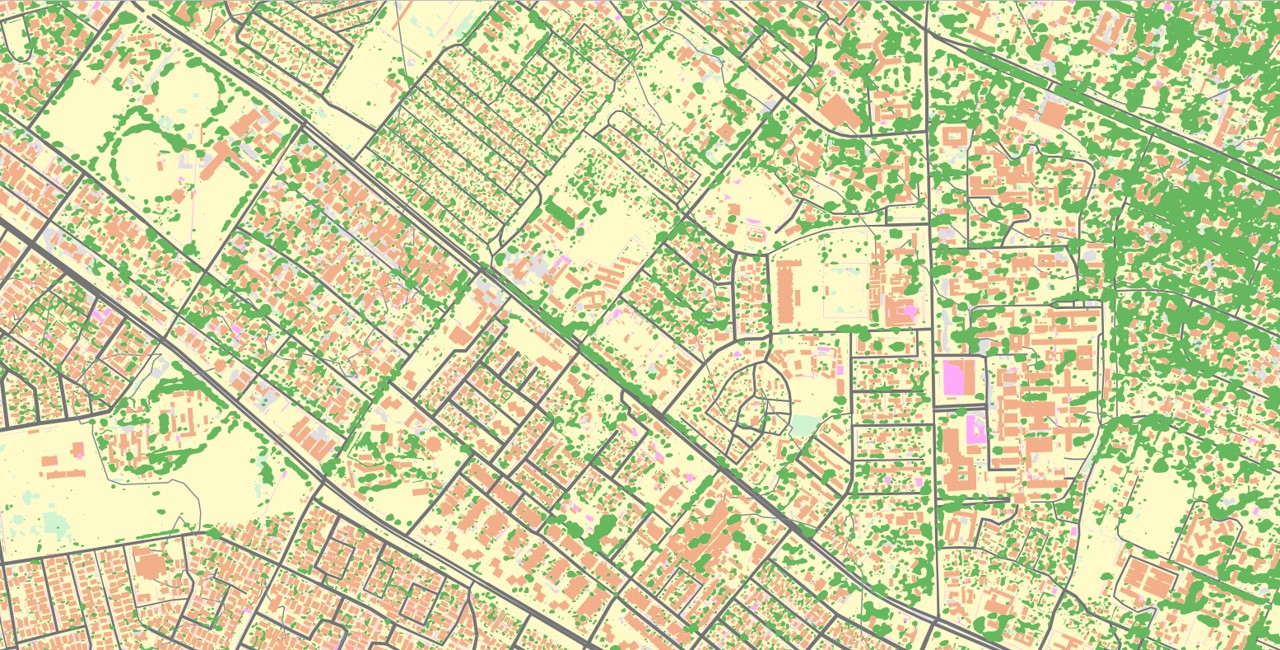
Precise digital mapping is essential for ensuring connectivity, charting economic growth, outlining demographic patterns, and getting a bird-eye view of resource concentration and allocation. It is a powerful visual tool for policymakers to tackle skewed development patterns, address social disparity, and craft sustainable policies.
Last year, Ordnance Survey, UK’s national mapping agency, partnered with the government of Zambia to create an AI-based digital base map of the capital Lusaka. The Zambia Ministry of Lands and Natural Resources, Zambia Ministry of Local Government, International Growth Centre, and Commonwealth Association of Architects, were involved in the project.
The Zambian authorities are using these maps for effective investment planning, monitoring, and identifying shortfalls in the country’s public infrastructure. They are also being used to improve access to healthcare and provide proper sanitation facilities.
Basemap Lusaka
Rampant urbanization and haphazard growth of settlements is leading to lack of basic facilities such as access to water, electricity, sanitation, connectivity and other public utilities. With accurate data-driven insights and aerial imagery, the government gets a clear picture of the sprawl and can take action accordingly.
Lusaka is a bustling commercial city as well as the seat of Zambia’s government. It is among the fastest growing cities in southern Africa with a population of over three million.

As per estimates, 70% of the city’s population dwells in informal settlements, which can be formalized with highly precise and accurate mapping, leading to citizen empowerment and rapid strides in land administration and tenure. Digital maps are also playing a role in better transport planning.
“Introducing OS’s AI-capable basemap has unlocked new capabilities in geospatial analysis to support policy planning and decisions. It has enabled the Ministry of Lands and Natural Resources to quickly update its maps and to create different, thematic maps using AI capabilities”, says Dr. Emmanuel Tembo, Head of Land Titling, Zambia Ministry of Lands and Natural Resources.
“OS’s ground-breaking technology means that our Government can make informed decisions quickly about numerous issues including urban housing policy and climate change adaptation issues”, he adds.
Global lessons
The OS basemap of Lusaka provides insights on informal settlements and is helpful in sustainable urban development to meet the basic needs of citizens.
“Our creation of a scalable, replicable, digital base map is not only relevant to cities such as Lusaka. It has far-reaching benefits; nationally, regionally, and even globally. It provides crucial information on aspects such as population and density, the number of built structures, the location of infrastructure including water and energy supplies. To better target investment. To improve the application and development of services”, says Juliet Ezechie, Head of International at OS.
“Detailed mapping is essential for meeting the challenges of urban living and can be a powerful tool for transformational change in sustainable cities. Understanding the true nature of the real world leads to informed decisions that can improve quality of life for citizens”, she adds.
OS created the base map from aerial imagery, using an automated process. Machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) enabled OS to teach a computer system to look for, label, and vectorise features in images, using training data. Such features included Roofed Structures, Natural Surface, Sealed Surface, Roads (including road networks), grass, trees and water.